2026 Social Security Changes: What Retirees Need to Know

Navigating 2026 Social Security changes requires retirees to understand forthcoming benefit adjustments and eligibility modifications to effectively plan their financial future.
For many Americans, Social Security represents a cornerstone of their retirement security, a promise of financial stability after decades of work. However, the system is not static; it undergoes periodic reviews and adjustments to ensure its long-term viability. As we approach 2026, significant discussions and potential reforms are on the horizon. Understanding these potential shifts is paramount for current retirees and those nearing retirement. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to
Navigating 2026 Social Security Changes: What Retirees Need to Know About Benefit Adjustments and Eligibility, empowering you with the knowledge to prepare effectively.
Understanding the Landscape of Social Security in 2026
The Social Security Administration (SSA) continuously monitors the program’s financial health, making projections and recommending adjustments to Congress. As 2026 draws closer, the focus intensifies on ensuring the program’s solvency for future generations while maintaining its commitment to current beneficiaries. This involves a delicate balance of economic realities, demographic shifts, and political considerations.
Several factors contribute to the ongoing need for Social Security reform. A key challenge is the changing demographics of the United States. With a growing number of retirees and a relatively slower growth in the working population, the dependency ratio—the number of retirees supported by each worker—is increasing. This puts strain on the pay-as-you-go system, where current workers’ contributions fund current retirees’ benefits.
Demographic Shifts and Their Impact
- Aging Population: The Baby Boomer generation continues to enter retirement, leading to a larger beneficiary pool.
- Lower Birth Rates: Fewer new workers are entering the workforce to replenish the trust funds.
- Increased Longevity: People are living longer, meaning they collect benefits for an extended period.
These demographic trends necessitate a re-evaluation of how Social Security is funded and how benefits are distributed. The goal is to ensure that the program remains a vital safety net for all Americans, adapting to the evolving socio-economic landscape. Understanding these foundational pressures helps in grasping the rationale behind potential changes.
In essence, the discussions surrounding 2026 Social Security changes are not just about numbers; they are about maintaining a societal promise. The adjustments being considered are designed to address these long-term financial challenges, ensuring that the system can continue to provide essential support for millions of Americans in their golden years.
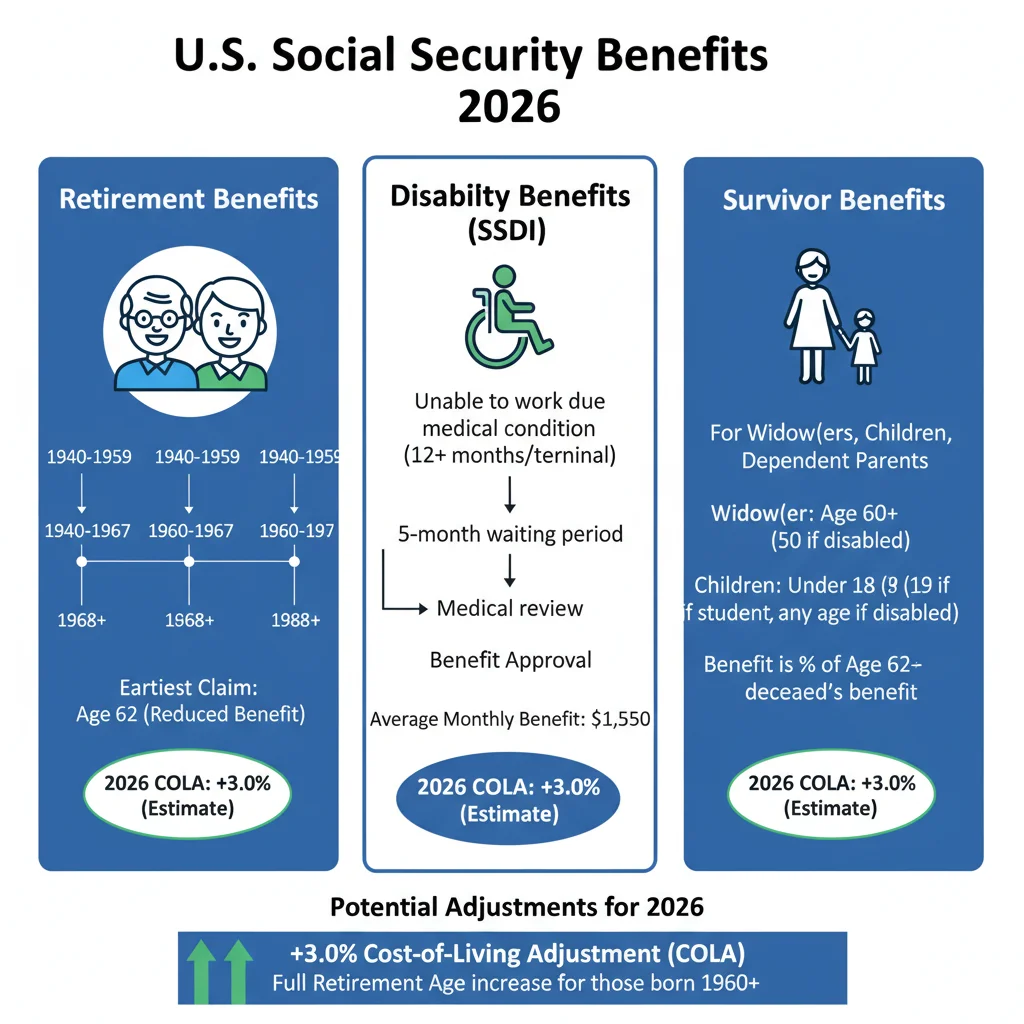
Potential Benefit Adjustments for Retirees
One of the most immediate concerns for retirees revolves around potential shifts in their benefit payments. While specific legislative proposals are still under debate, several avenues for adjustment are commonly discussed. These could range from alterations to the Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) formula to changes in how benefits are calculated based on earnings history.
The COLA is a critical component of Social Security, designed to ensure that benefits keep pace with inflation. Historically, COLA has been tied to the Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W). However, alternative inflation measures, which could result in different annual adjustments, are sometimes proposed. Any modification to the COLA formula would directly impact the purchasing power of retirees’ benefits over time.
Key Areas of Benefit Adjustment Consideration
- COLA Formula Changes: Exploring alternative inflation indices that might yield lower or higher annual adjustments.
- Benefit Formula Modifications: Potential adjustments to how Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME) are calculated, which directly influences initial benefit amounts.
- Progressive Indexing: Proposals to adjust benefits based on an individual’s lifetime earnings, potentially offering more to lower-income retirees and less to higher-income ones.
These potential adjustments highlight the dynamic nature of Social Security. While the intent is often to strengthen the program, individual retirees must stay informed about how these changes might specifically affect their monthly income. Proactive financial planning, including diversifying retirement income sources, becomes even more critical in this evolving environment.
The impact of any benefit adjustments will vary depending on individual circumstances, including age, earnings history, and other sources of retirement income. It is essential for retirees to monitor legislative developments closely and consult with financial advisors to understand the personalized implications of these potential changes. Maintaining an adaptable financial plan is key to navigating these uncertainties successfully.
Eligibility Criteria: What Could Change in 2026?
Beyond benefit amounts, modifications to eligibility criteria are also frequently debated as part of broader Social Security reform efforts. These changes could affect when individuals can claim benefits, the number of work credits required, or even the definition of retirement itself. Such adjustments aim to align the program’s payouts with its financial capacity.
One prominent area of discussion involves the Full Retirement Age (FRA). The FRA, which determines when an individual can receive 100% of their earned benefits, has gradually increased over the years. For those born in 1960 or later, it is currently 67. There are often proposals to further increase the FRA, reflecting longer life expectancies. A higher FRA would mean individuals would either have to work longer or accept reduced benefits if they claim earlier.
Potential Eligibility Modifications
- Raising the Full Retirement Age (FRA): Incrementally increasing the age at which full benefits can be claimed.
- Adjusting Early Retirement Age: While less common, changes to the earliest age one can claim (currently 62) could also be considered.
- Work Credit Requirements: Though unlikely for 2026, future discussions might include increasing the number of work credits needed to qualify for benefits.
These potential changes to eligibility criteria underscore the importance of understanding your personal claiming strategy. Deciding when to claim Social Security benefits is one of the most significant retirement planning decisions, and any shifts in eligibility rules could alter optimal claiming ages for future retirees. Early planning and consultation with the SSA or a financial expert are highly recommended.
For current retirees, changes to the FRA would likely not directly impact their already claimed benefits. However, those nearing retirement, particularly individuals in their late 50s and early 60s, should pay close attention to these discussions. Understanding how eligibility might evolve will allow for timely adjustments to retirement timelines and financial projections, ensuring a smoother transition into retirement.
The Impact of Economic Factors on Social Security
Social Security’s financial health is inextricably linked to the broader U.S. economy. Economic performance, including inflation, wage growth, and employment rates, directly influences the program’s income and expenditures. As 2026 approaches, the prevailing economic climate will play a significant role in shaping the urgency and nature of any reforms.
Wage growth, for instance, is crucial because Social Security’s primary funding comes from payroll taxes. Strong wage growth means higher tax contributions, bolstering the trust funds. Conversely, periods of stagnant wages can strain the system. Similarly, high unemployment reduces the number of contributors, further impacting the program’s revenue stream.
Economic Variables Influencing Social Security
- Inflation Rates: Directly affects COLA, impacting the real value of benefits for retirees.
- Wage Growth: Determines the revenue stream from payroll taxes, which fund current benefits.
- Interest Rates: Affects the earnings of the Social Security Trust Funds’ investments.
- Employment Levels: Higher employment means more workers contributing to the system.
The interplay of these economic factors creates a complex environment for Social Security planning. A robust economy can provide a buffer, potentially delaying the need for more drastic reforms. However, economic downturns can accelerate the timeline for necessary adjustments. Retirees should be aware that the economic outlook is a key determinant of the program’s stability and future changes.
Understanding the economic backdrop helps in comprehending why certain proposals gain traction. Policymakers often look for solutions that are economically sustainable while minimizing adverse impacts on beneficiaries. Therefore, staying informed about economic forecasts and their potential implications for Social Security is an important aspect of prudent retirement planning.
Preparing for Changes: Strategies for Retirees
Given the potential for Social Security changes in 2026, proactive preparation is essential for retirees and those nearing retirement. Relying solely on Social Security for retirement income can be risky, making diversification and strategic financial planning more important than ever. This preparation involves reviewing current financial situations and exploring various avenues to enhance financial security.
One fundamental strategy is to assess your current retirement income sources. This includes pensions, 401(k)s, IRAs, savings accounts, and any other investments. Understanding the total picture allows you to identify potential gaps if Social Security benefits are adjusted. Diversifying these income streams can provide a hedge against any single source being negatively impacted.
Actionable Steps for Retirement Planning
- Review Your Financial Plan: Regularly assess your budget, expenses, and income sources to identify areas for adjustment.
- Maximize Other Retirement Accounts: Contribute as much as possible to 401(k)s, IRAs, and other tax-advantaged accounts.
- Consider Working Longer: If feasible, delaying retirement can increase your Social Security benefits and allow more time for savings to grow.
- Consult a Financial Advisor: Seek professional guidance to create a personalized strategy that accounts for potential Social Security changes.
Another crucial step is to stay informed about legislative developments. The Social Security Administration’s website and reputable financial news sources are excellent resources for tracking proposed changes. The more informed you are, the better equipped you will be to make timely adjustments to your retirement strategy.
Ultimately, preparing for 2026 Social Security changes involves a holistic approach to retirement planning. By taking proactive steps to diversify income, manage expenses, and stay informed, retirees can better navigate any forthcoming adjustments and maintain their financial well-being throughout their golden years.
Advocacy and Future Outlook for Social Security
The future of Social Security is not solely determined by economic forces or legislative mandates; it is also shaped by public discourse and advocacy. Various organizations and interest groups actively engage in discussions about the program’s future, representing the interests of retirees, workers, and taxpayers. Understanding these differing perspectives can provide insight into the potential trajectory of reforms.
Advocacy groups for seniors, for example, often campaign for protecting current benefit levels and ensuring that any reforms do not disproportionately affect vulnerable populations. Conversely, some fiscal conservative groups may advocate for more significant structural changes, including raising the retirement age or adjusting benefit formulas more aggressively, to ensure long-term solvency.
Key Voices in the Social Security Debate
- AARP: Advocates for the interests of older Americans, focusing on protecting Social Security benefits.
- National Committee to Preserve Social Security and Medicare: Works to ensure the long-term solvency and adequacy of both programs.
- Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget: Proposes solutions to improve the nation’s fiscal health, often including Social Security reforms.
The political landscape surrounding Social Security is often complex, with bipartisan agreement proving challenging. However, the recognition of the program’s importance to millions of Americans means that discussions will continue to evolve, seeking solutions that balance fiscal responsibility with social welfare. Retirees and future beneficiaries have a vested interest in following these debates.
The long-term outlook for Social Security remains a topic of ongoing discussion. While challenges exist, the fundamental commitment to providing a safety net for retirees, the disabled, and survivors is deeply ingrained in American policy. By understanding the various viewpoints and staying engaged with the conversation, individuals can better anticipate and adapt to the future of this vital program.
| Key Topic | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Benefit Adjustments | Potential changes to COLA formulas or how initial benefits are calculated, impacting retirees’ monthly income. |
| Eligibility Criteria | Discussions around raising the Full Retirement Age (FRA) or adjusting work credit requirements. |
| Economic Impact | Inflation, wage growth, and employment rates significantly influence Social Security’s financial solvency. |
| Preparation Strategies | Diversifying income, maximizing retirement accounts, and seeking financial advice are crucial for adaptation. |
Frequently Asked Questions About 2026 Social Security Changes
While definitive reductions for current beneficiaries are not typically the primary focus of reforms, changes to the Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) formula could impact the rate at which your benefits increase, effectively reducing their purchasing power over time. Direct cuts are generally less common.
Proposals often suggest a gradual increase in the Full Retirement Age (FRA) to reflect longer life expectancies. While unlikely to dramatically shift for those already retired, individuals nearing retirement may see their FRA adjusted upward, requiring them to work longer for full benefits.
Inflation is a critical factor, as it directly influences the Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA). If the COLA formula is modified to use a different inflation index, the annual increase in benefits could change. This directly impacts the real value of Social Security payments for retirees.
To prepare, review your overall retirement plan, diversify your income sources beyond Social Security, and consider maximizing contributions to other retirement accounts. Staying informed about legislative developments and consulting with a financial advisor are also crucial steps.
The official Social Security Administration (SSA) website is the most reliable source for updates and information. Additionally, reputable financial news outlets and non-partisan organizations specializing in retirement research often provide accurate and timely analyses of proposed changes.
Conclusion
As we look towards 2026, the ongoing discussions and potential reforms to Social Security underscore the dynamic nature of this vital program. While the specifics of any changes remain subject to legislative processes and economic conditions, understanding the underlying pressures and proposed solutions is crucial for every retiree and future beneficiary. Proactive engagement, diligent financial planning, and continuous education about these developments will empower individuals to navigate any adjustments effectively, ensuring a secure and stable retirement. The future of Social Security is a collective responsibility, and staying informed is the first step toward safeguarding its promise for generations to come.





